Detection rules as code

With the introduction of the msgraph-provider, it is now quite easy to deploy your custom detection rules to Microsoft Defender fully automatically using Terraform.
The immediate benefit of doing this is that in addition to easily deploy large rulesets across tenants, you also get version control on all detection rules with an easy way of rolling back in case of errors.
Before you can deploy detection rules, you need to set up permissions in Entra - specifically CustomDetection.ReadWrite.All in Microsoft Graph.
If this is something you already know - Skip to the Terraform goodies!
Or if you prefer to just see the finished code: https://github.com/FrodeHus/tf-custom-detection-rules-demo
Create application with necessary permissions
Microsoft Graph API is our gateway to deploy custom detection rules and we need to grant permissions specifically for this.
So, we need to create a Entra ID Application that grants the Graph permission CustomDetection.ReadWrite.All.
Since creating application in Entra ID using the Azure Portal is pretty much always used, I'll show the command-line route this time - mostly as my own little note.
The command-line route
Create a file named manifest.jsonwith the following content:
{
"requiredResourceAccess": [
{
"resourceAppId": "00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000",
"resourceAccess": [
{
"id": "e0fd9c8d-a12e-4cc9-9827-20c8c3cd6fb8",
"type": "Role"
}
]
}
]
}
The id e0fd9c8d-a12e-4cc9-9827-20c8c3cd6fb8 indicates the permission CustomDetection.ReadWrite.All.
We can now create this application using the Azure CLI by issuing the command:
az ad app create --display-name "Custom detection rule demo" --required-resource-accesses @manifest.json This returns a JSON value that looks like this:
{
"@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/$metadata#applications/$entity",
"addIns": [],
"api": {
"acceptMappedClaims": null,
"knownClientApplications": [],
"oauth2PermissionScopes": [],
"preAuthorizedApplications": [],
"requestedAccessTokenVersion": null
},
"appId": "8697414f-ceb8-4517-ba9a-8fce57ef617a",
"appRoles": [],
...
}Take note of the value in appId - we'll use this next.
Before the application is allowed to use this permission, we need to grant consent as an administrator.
Again, we can do this using the Azure CLI (using the appId noted above):
az ad app permission admin-consent --id 8697414f-ceb8-4517-ba9a-8fce57ef617a
Finally, we need some credentials so we just ask for a password reset:
az ad app credential reset --id 8697414f-ceb8-4517-ba9a-8fce57ef617a
This returns with our password for the service principal we've just created:
{
"appId": "8697414f-ceb8-4517-ba9a-8fce57ef617a",
"password": "<autogenerated password>",
"tenant": "<tenant id>"
}Terraform the rules
The msgraph provider is quite nice in that it is quite dynamic and you don't have to wait for the developers to add specific support for a resource - if it exists in the Graph API, you can already use it. More on this below.
Setting up the provider
Create a file name providers.tf (you can use this for all your providers, but we'll just use msgraphhere)
terraform {
required_providers {
msgraph = {
source = "microsoft/msgraph"
}
}
}
provider "msgraph" {
client_id = var.client_id
tenant_id = var.tenant_id
client_secret = var.client_secret
}Create a variables.tf file to hold our variable definitions:
variable "client_id" {
type = string
}
variable "tenant_id" {
type = string
}
variable "client_secret" {
type = string
}Then supply our service principal credentials in a terraform.tfvars file - the benefit being that you can exclude this file from source control and not leak your secrets:
client_id = "<client/app id>"
tenant_id = "<tenant id>"
client_secret = "<the super secret password>"Run terraform init to install it.
Creating your first custom detection rule
The general template for a msgraph resource looks like this:
resource "msgraph_resource" "<name of the resource>" {
url = "<graph api relative url>"
api_version = "<this defaults to v1.0 and is optional>"
body = {
... the main payload for the specific resource ...
}
}As mentioned, we don't need specific support for resource types - we just need to know the relative Graph API URL where the endpoint resides and the shape of the request.
Since /security/rules/detectionRules is where the custom detection rules live and it is currently only in beta our base template for a detection rule looks like this (based on this documentation):
resource "msgraph_resource" "my_rule" {
url = "security/rules/detectionRules"
api_version = "beta"
body = {
...
}
}
}Finally, we can create an actual complete custom detection rule (add in a new file eicar_test_rule.tf:
resource "msgraph_resource" "eicar_test_file" {
url = "security/rules/detectionRules"
api_version = "beta"
body = {
displayName = "EICAR testfile detected"
isEnabled = true
schedule = {
period = "1H"
}
queryCondition = {
queryText = "DeviceFileEvents\n| where SHA1 == \"811c4081aa56bd8182391934c6c0febed05d9efc\""
}
detectionAction = {
organizationalScope = null
alertTemplate = {
title = "EICAR testfile detected"
description = "The EICAR testfile was detected - red alert!"
severity = "high"
category = "Malware"
mitreTechniques = []
recommendedActions = null
impactedAssets = [
{
"@odata.type": "#microsoft.graph.security.impactedDeviceAsset",
identifier = "deviceId"
}
]
}
}
}
}By creating separate files for each rule, you can build a library of your detections and easily maintain each of them.
Deploying the rules
Once everything is in place, all we need to do is run terraform apply and our rule(s) will be deployed.
Terraform will perform the following actions:
...
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
msgraph_resource.eicat_test_file: Creating...
msgraph_resource.eicar_test_file: Creation complete after 1s [id=3057]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.Now, if we wish to update these we can just update the rule files and do another terraform apply and Terraform will update the already deployed rules (and deploy any new ones).
You can view all your custom detection rules in the Defender portal:
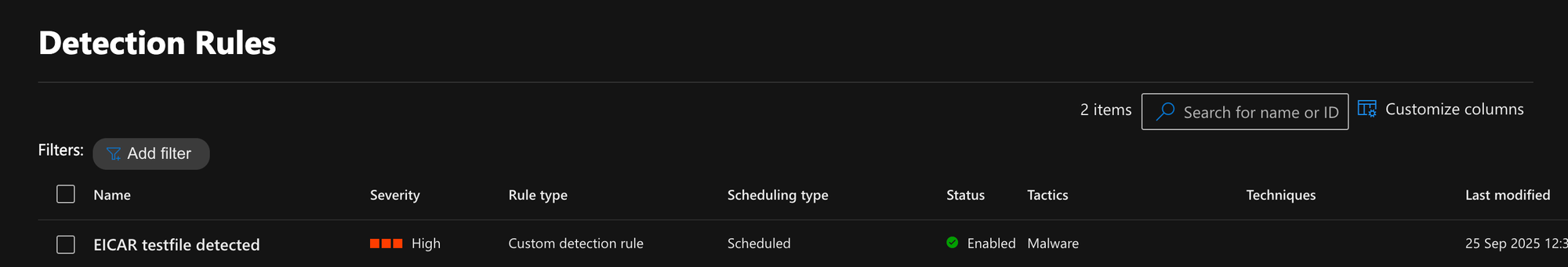
Finished code: https://github.com/FrodeHus/tf-custom-detection-rules-demo
Hope this was helpful!
